Unleashing the Potential of Solar Power for Home
Introduction to Solar Power for Homes
- The rising importance of renewable energy sources
- Understanding solar power as a viable solution for homes
- Benefits of solar power for homeowners
With the increasing global focus on sustainability and reducing carbon emissions, the importance of renewable energy sources has never been greater. Solar power, in particular, has emerged as a viable solution for homeowners seeking to embrace sustainable living. By harnessing the power of the sun, solar energy offers numerous benefits, both environmentally and economically.
How Solar Power Works
- Explaining the photovoltaic effect
- Understanding solar panels and their components
- Grid-tied vs. off-grid solar systems
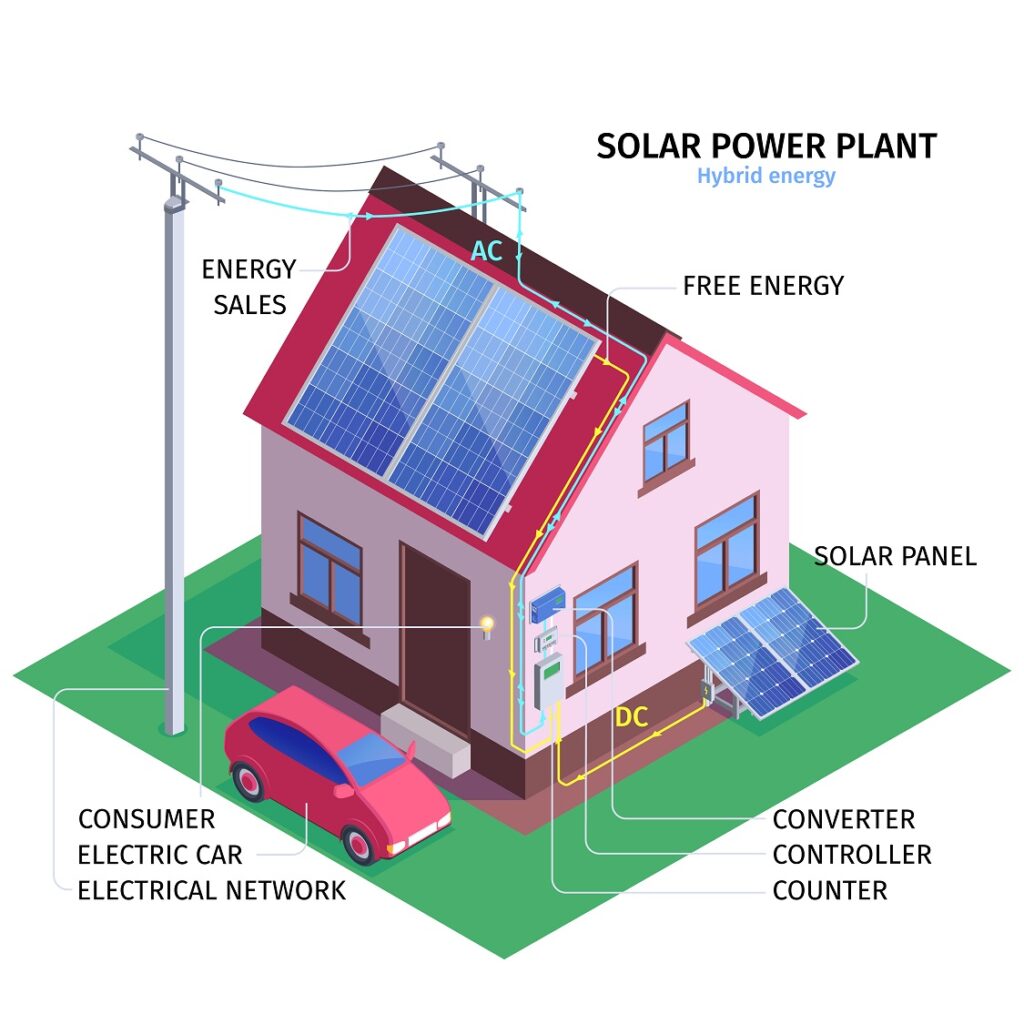
At the heart of solar power lies the photovoltaic effect, which converts sunlight into electricity through the use of solar panels. These panels consist of interconnected solar cells made from semiconductors, such as silicon. When sunlight strikes these cells, it excites the electrons, creating a flow of direct current (DC) electricity. The solar panels are then connected to an inverter, which converts DC electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity for use in homes.
There are two main types of solar systems: grid-tied and off-grid. Grid-tied systems allow homeowners to remain connected to the electrical grid while generating their own solar power. Excess energy can be fed back into the grid, earning credits or monetary compensation. Off-grid systems, on the other hand, are entirely independent and rely on solar panels and batteries to meet all their energy needs.
Determining Solar Suitability for Your Home
- Assessing available sunlight
- Estimating energy consumption and potential savings
- Evaluating roof space and orientation
Before investing in solar power for your home, it’s essential to determine its suitability. One key factor to consider is the amount of sunlight available in your location. Ideally, homes with unobstructed access to sunlight throughout the day are more suitable for solar installations.
Additionally, assessing your energy consumption and potential savings is crucial in determining the size of the solar system needed. By understanding your energy usage patterns, you can tailor your solar power system to meet your specific needs and maximize savings.
Another consideration is evaluating your roof space and orientation. Solar panels are typically installed on rooftops to maximize exposure to sunlight. A south-facing roof with a slope of 30 to 45 degrees is ideal for optimal solar energy generation.
Steps to Installing Solar Power at Home
- Conducting a solar energy audit
- Choosing the right solar panel system
- Understanding permits and regulations
- Hiring a reputable solar installer

Installing solar power at home involves several essential steps. To begin, consider conducting a solar energy audit to assess the feasibility of solar power for your specific property. This audit takes into account factors such as available sunlight, energy consumption, and the structural integrity of your home.
Once you’ve determined the viability of solar power for your home, it’s time to choose the right solar panel system. Factors such as efficiency, durability, and cost should be considered when selecting the most suitable panels for your needs.
It’s important to familiarize yourself with permits and regulations governing solar installations in your area. Depending on your location, you may need to obtain permits and adhere to specific guidelines to ensure a smooth installation process.
Finally, it’s crucial to hire a reputable solar installer who has the necessary expertise and experience with solar power systems. Research and compare different installers, looking for certifications and customer reviews, to ensure a successful installation.
Types of Solar Panels for Residential Usage

- Monocrystalline vs. polycrystalline solar panels
- Comparing thin-film and concentrated solar panels
- Evaluating the efficiency and durability of solar panels
When considering solar panels for residential usage, homeowners can choose from various types. Monocrystalline panels are made from a single silicon crystal and offer high efficiency and durability. Polycrystalline panels, on the other hand, are made from several silicon crystals, resulting in a slightly lower efficiency but a more cost-effective option.
In addition to monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels, there are thin-film and concentrated solar panels. Thin-film panels are flexible and can be integrated into various surfaces, making them suitable for unconventional installations. Concentrated solar panels use lenses or mirrors to focus sunlight onto smaller, highly efficient solar cells.
Efficiency and durability are crucial considerations when evaluating solar panels. The efficiency of a panel refers to its ability to convert sunlight into electricity, while durability ensures its longevity and resistance to environmental factors.
Solar Inverters: The Heart of Your Solar System
- Understanding the role of solar inverters
- Differentiating between string, central, and microinverters
- Evaluating inverter efficiency and monitoring capabilities
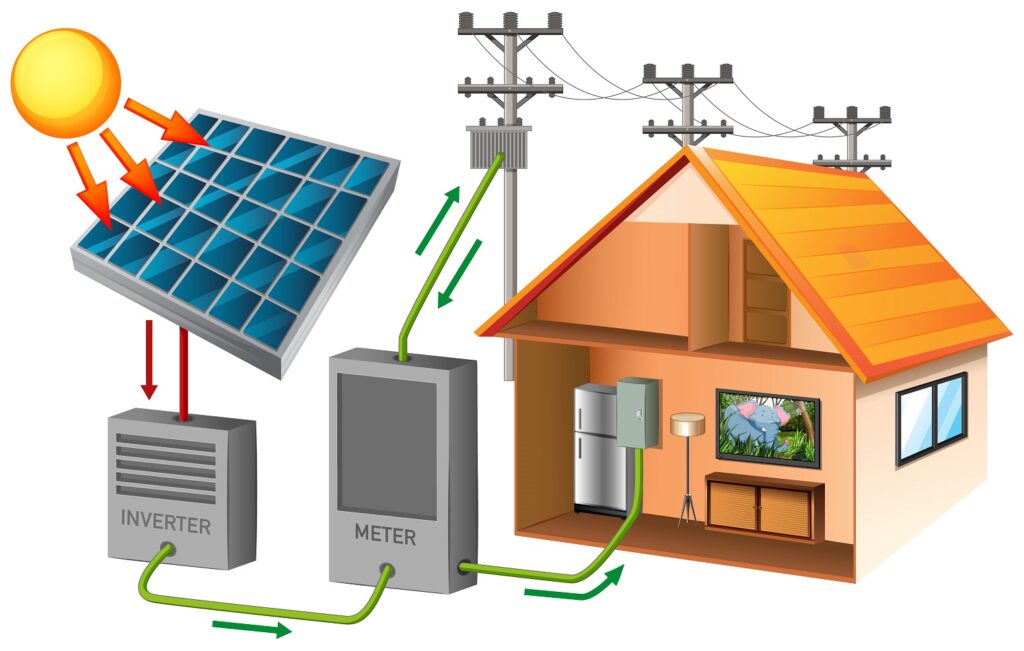
While solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity, solar inverters play a crucial role in transforming that electricity into a form usable in homes. Inverters convert the direct current (DC) electricity produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, matching the form required for powering household appliances.
There are different types of inverters available, including string, central, and microinverters. String inverters are commonly used in residential settings and connect multiple solar panels in a series. Central inverters, typically used in larger installations, connect to a centralized array of panels. Microinverters, on the other hand, are installed on each individual solar panel, maximizing energy production from each module.
Efficiency and monitoring capabilities are essential factors to consider when selecting an inverter. Higher efficiency ensures minimal energy loss during the conversion process, maximizing the overall output of your solar system. Monitoring capabilities provide homeowners with real-time data on energy production, allowing for better system management and optimization.
Solar Batteries: Storing Excess Energy for Later Use
- Introduction to solar battery technology
- Comparing lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries
- Benefits of integrating solar batteries into your system
In addition to solar panels and inverters, solar battery technology can further enhance the efficiency and sustainability of your solar power system. Solar batteries store excess energy generated by the panels for later use, ensuring a continuous power supply even when sunlight is scarce.
Two common types of solar batteries are lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries. Lead-acid batteries are more affordable but have a shorter lifespan and lower energy density. In contrast, lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density, longer lifespan, and greater efficiency, albeit at a higher cost.
Integrating solar batteries into your system provides several benefits. Firstly, it allows you to store excess energy generated during the day and use it during peak demand or when sunlight is limited. This effectively reduces reliance on the electrical grid and maximizes the self-consumption of solar power.
Maximizing Solar Power Efficiency
- Implementing proper system sizing and design
- Utilizing tracking systems and tilt mechanisms
- Ensuring regular maintenance and cleaning of solar panels
To optimize the benefits of solar power, it is crucial to focus on maximizing the efficiency of your system. Proper system sizing and design considerations ensure that your solar panels can generate enough electricity to meet your energy needs without overproduction.
Tracking systems and tilt mechanisms can further enhance solar power efficiency by allowing the panels to follow the sun’s path throughout the day. This optimizes sunlight exposure and increases energy generation potential.
Regular maintenance and cleaning of solar panels are essential for optimal performance. Dust, dirt, and debris can hinder the absorption of sunlight by the panels, resulting in decreased efficiency. By maintaining a clean surface and promptly addressing any maintenance issues, homeowners can ensure their solar power system operates at its best.
Financial Incentives and Return on Investment
- Exploring available government incentives and grants
- Understanding net metering and feed-in tariffs
- Calculating payback periods and lifetime savings
One significant advantage of investing in solar power for homes is the potential for financial incentives and a return on investment. Many governments offer incentives, such as tax credits, rebates, and grants, to encourage the adoption of solar energy. By exploring these incentives, homeowners can significantly reduce the upfront costs of installation.
Net metering and feed-in tariffs are additional financial benefits associated with solar power. Net metering allows homeowners to sell excess energy back to the grid, effectively offsetting their energy bills. Feed-in tariffs, on the other hand, involve receiving payment for the excess energy fed into the grid.
Calculating the payback period and lifetime savings provides homeowners with an understanding of the long-term financial benefits of investing in solar power. By comparing the upfront investment with the potential savings on energy bills over time, homeowners can make informed decisions about the viability of solar power for their specific situation.
Environmental Benefits of Solar Power for Homes
- Contribution to reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- Mitigating climate change impacts
- Preserving natural resources and ecosystems
Apart from the financial advantages, solar power for homes offers significant environmental benefits. By relying on clean, renewable energy, homeowners contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, a primary cause of climate change. Solar power reduces reliance on fossil fuel-based electricity, mitigating the environmental impact associated with their extraction and combustion.
Solar energy also helps mitigate the impacts of climate change, such as increased temperatures and extreme weather events. By embracing solar power, homeowners become part of a sustainable solution, working towards a more environmentally resilient future.
Furthermore, solar power contributes to the preservation of natural resources and ecosystems. By reducing the demand for electricity generated from non-renewable sources, solar power reduces the need for extracting finite resources like coal, oil, and natural gas. This, in turn, helps protect biodiversity and fragile ecosystems affected by resource extraction.
Overcoming Challenges and Potential Limitations
- Addressing intermittent power supply issues
- Sustaining solar power during unfavorable weather conditions
- Dealing with system maintenance and repair challenges
While solar power offers numerous advantages, there are also challenges and limitations to consider. One common challenge is the intermittent power supply due to the reliance on sunlight. During cloudy days or at night, solar power generation decreases, requiring homeowners to rely on alternatives such as the electrical grid or a backup power source.
Unfavorable weather conditions, such as heavy rainfall or snowfall, can also affect solar power generation by blocking sunlight or impeding the maintenance of rooftop solar panels. Proactive measures, such as regular cleaning, can help mitigate these challenges and maintain optimal performance.
System maintenance and repair challenges are inherent in any technology. While solar power systems are generally durable and low-maintenance, occasional repairs or component replacements may be necessary. Homeowners should be prepared for these eventualities and consider the warranty and post-installation support provided by the solar installer when selecting a system.
Integration with Smart Home Technology
- Connecting solar power with energy management systems
- Optimizing energy consumption through smart home automation
- Future possibilities of solar-powered smart homes
Solar power can integrate seamlessly with smart home technology, offering additional energy management and efficiency advantages. By connecting solar power to energy management systems, homeowners can monitor and control their energy consumption in real-time. This allows for better optimization of energy usage, further reducing reliance on the electrical grid.
Smart home automation takes energy optimization a step further. By integrating solar power with devices such as smart thermostats, lighting controls, and other appliances, homeowners can achieve greater energy efficiency. These systems can automatically adjust settings to maximize energy usage during daylight hours and minimize consumption during non-peak times.
The future holds exciting possibilities for solar-powered smart homes. With advancements in energy storage technology and the integration of artificial intelligence, solar systems can become more autonomous and efficient. This could lead to increased energy independence and further reductions in carbon emissions.
Case Studies: Real-Life Solar Home Installations
- Residential solar success stories
- Lessons learned from practical implementations
- Impact of solar power on homeowners’ lives
Real-life case studies provide valuable insights into the practicalities and benefits of solar home installations. Residential solar success stories showcase the transformative power of solar energy in reducing energy costs, increasing self-sufficiency, and making a positive environmental impact.
These case studies offer valuable lessons, such as the importance of proper system sizing, regular maintenance, and realistic expectations regarding energy generation and savings. By learning from the experiences of others, homeowners can make more informed decisions and plan for a successful solar power installation.
The impact of solar power on homeowners’ lives extends beyond the financial and environmental realm. Solar energy empowers individuals to take control of their energy consumption and reduce their carbon footprint. It instills a sense of pride and fulfillment in knowing that one’s home is contributing to a more sustainable future.
Solar Power for Homes around the World
- Global initiatives and policies promoting solar energy
- Case studies from different countries
- Lessons for widespread adoption and implementation
Solar power is not limited to specific regions or countries. It is a global movement driven by both grassroots initiatives and government policies promoting renewable energy. The adoption of solar power varies worldwide, with some countries leading the way in solar installations and others experiencing rapid growth.
Case studies from different countries demonstrate the potential of solar power and provide valuable insights into its widespread adoption and implementation. By examining successful solar initiatives, lessons can be learned and applied in regions where solar power is still in the early stages of development.
By embracing solar power on a global scale, countries can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, lower carbon emissions, and create a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the typical cost of installing solar power at home?
- How long do solar panels last and how do I maintain them?
- Can solar power be used during power outages?
- How does solar power affect property value?
- Is my home suitable for solar power if I live in a cloudy region?
It is natural for homeowners to have questions about solar power before making the decision to invest. Here are some frequently asked questions to address common concerns and provide clarity:
- What is the typical cost of installing solar power at home? The cost of installing solar power at home varies depending on factors such as system size, location, and available incentives. On average, homeowners can expect to invest between $10,000 and $30,000 for a residential solar system.
- How long do solar panels last and how do I maintain them? Solar panels are built to withstand harsh weather conditions and come with warranties lasting 25 to 30 years. With proper maintenance, such as regular cleaning and inspection, solar panels can continue to generate electricity efficiently throughout their lifespan.
- Can solar power be used during power outages? Traditional grid-tied solar power systems are automatically shut off during power outages for safety reasons. However, with the addition of a backup power source, such as solar batteries or a generator, homeowners can still access electricity during blackouts.
- How does solar power affect property value? Solar power installations can increase the value of a property. Studies have shown that homes equipped with solar panels sell at a premium, as potential buyers appreciate the long-term savings and environmental benefits associated with solar energy.
- Is my home suitable for solar power if I live in a cloudy region? Solar power generation is still possible in cloudy regions, although the energy output may be lower compared to sunnier areas. Advances in solar panel technology have improved their efficiency, enabling them to capture even small amounts of sunlight and convert it into usable electricity.